What is a threat intelligence platform?
Reduce Response Time
Seamless Integration
Cost-Effective Protection
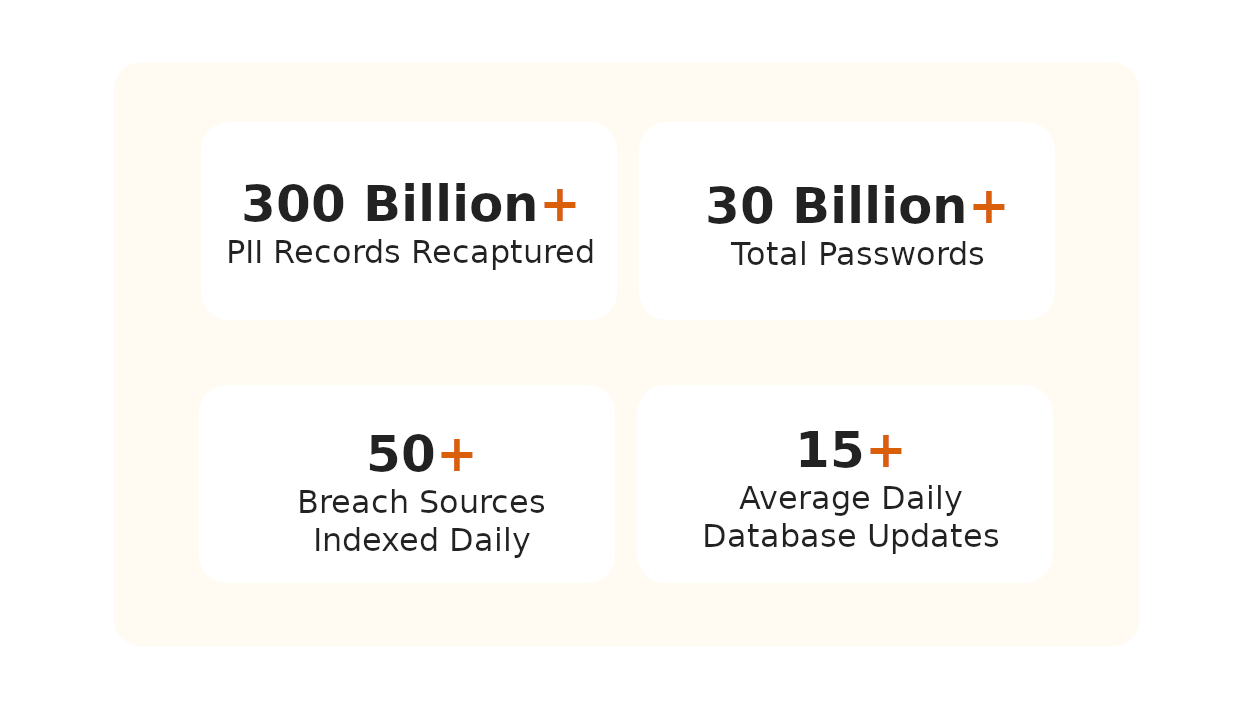
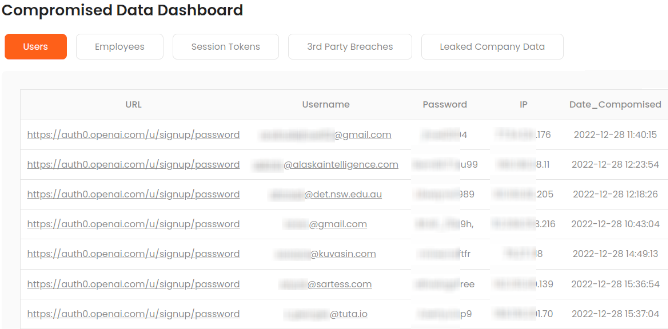
Monitor the Dark Web for Data Leakage with the #1 Platform Trusted by Great Companies from All Over the World
Our team uses Breachsense data to gain initial access during pen testing and red team engagements. The API is simple to use and the support is always helpful and responds quickly.
Our Security Colony platform relies on Breachsense data as part of our dark web monitoring service. The data is continuously updated and high quality. Highly recommend!
We rely on Breachsense for a lot of data. Their frequent database updates, constant availability, and handling of big and small breaches alike means we are always covered.
Breachsense Is Perfect For
Penetration Testers
Red Teams
Enterprise Security Teams
Incident Response Analysts
M&A Research
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a threat intelligence platform do?
A threat intelligence platform collects and analyzes cyber threat data from thousands of sources to identify potential risks targeting your organization. It automatically correlates the threat information with your specific assets to prioritize the most relevant threats. The platform then delivers actionable intelligence directly to your security team and existing security tools. This enables proactive threat detection and faster incident response. Essentially, it transforms raw threat data into clear, prioritized insights that help you prevent cyber attackers.
How to create a threat intelligence platform?
Start by defining your organization’s specific security objectives, critical assets, and threat landscape scope. Next, assemble a cross-functional team including cybersecurity analysts, threat hunters, and incident responders with clear roles and executive support. Build your data collection infrastructure by integrating multiple intelligence sources—commercial feeds, open-source intelligence (OSINT), government advisories, and industry-specific forums using threat intelligence platforms (TIPs) to aggregate and normalize the data. Develop an analysis workflow that evaluates threat relevance, impact, and likelihood. Implement an automated scoring and prioritization system to focus on the most critical risks. Finally, establish integrations with your existing incident response platform to share actionable intelligence with internal teams, executives, and external partners.
What are the three types of threat intelligence?
The three primary types of threat intelligence are Tactical, Operational, and Strategic. Each of these represent a different level of complexity and analysis depth. Tactical intelligence is technical and focused on the immediate future, dealing primarily with indicators of compromise (IOCs) like malicious IP addresses, URLs, file hashes, and domain names. Tactical threat intel can be automated and integrated into security tools. Operational intelligence provides deeper understanding of the “who,” “why,” and “how” behind attacks. It focuses on attribution, motivation, and the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) that threat actors use to plan and execute campaigns. Strategic intelligence offers a high-level perspective on how cyber threats intersect with global events, geopolitical conditions, and organizational risks. Strategic intelligence is typically used by executive leadership to guide cybersecurity investments and long-term decision-making.
What are the 5 stages of threat intelligence?
The threat intelligence lifecycle is made up of give interconnected stages. Together they transform raw data into actionable security insights. 1. Discovery aims to identify consumers’ intelligence requirements by defining objectives, determining what assets need protection, and establishing key performance indicators. 2. Collection involves gathering data from various sources including internal logs, external threat feeds, and open-source intelligence (OSINT) to meet the identified requirements. 3. Processing transforms collected data into a usable format by sorting, decrypting, and translating information to make it easier for analysts to work with effectively. 4. Analysis examines the processed data to identify patterns, anomalies, and signs of malicious activity by cross-referencing information from various sources and applying analytical techniques. 5. Dissemination distributes the analyzed intelligence to intended audiences in an actionable format, while Feedback gathers stakeholder input to continuously improve the entire threat intelligence process.